Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) have gained widespread attention due to their high biocompatibility, improved bioavailability, and enhanced therapeutic efficacy. These attributes support their broad range of applications in drug delivery.
As a result, several LNP-encapsulated therapeutics have received regulatory approval from both the FDA and EMA and are already available on the market. A prominent example demonstrating the potential of this technology is the COVID-19 mRNA vaccine, which relied on LNPs for efficient delivery and protection of the payload.
- IN VITRO CASE STUDY MRNA
The following in vitro study demonstrates that NovoArc’s lipids significantly enhance mRNA lipid nanoparticle (LNP) technology by improving both particle internalization and protein expression levels.
These findings suggest that NovoArc’s lipids may serve as promising next-generation components in LNP formulations, offering improved efficiency and stability compared to conventional systems.

Figure: Increased particle uptake and increased expression of GDGT (glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraether lipids) and ALE (archaeal lipid extract)-containing LNPs in C2C12 cells.
- IN VIVO TOXICITY STUDY
An extended single-dose toxicity study was conducted in Wistar rats to evaluate the safety of native GDGT and ionizable GDGT lipids after intramuscular (i.m.) administration. A total of 105 animals were included (10 + 5 animals per group), with a 14-day recovery period following a single 1 mg/kg dose in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, 2 mg/mL).
The results showed no mortality and no impact on feed consumption or body weight. Hematological parameters remained unchanged between treatment and control groups. Histopathological analysis revealed only mild to moderate local changes at the injection site, while no systemic effects were observed in any examined organs.
These findings clearly demonstrate that archaeal GDGT-based lipids are well tolerated and non-toxic, supporting their use in advanced drug delivery applications.
- IN VIVO PHARMACOKINETICS CASE STUDY MRNA
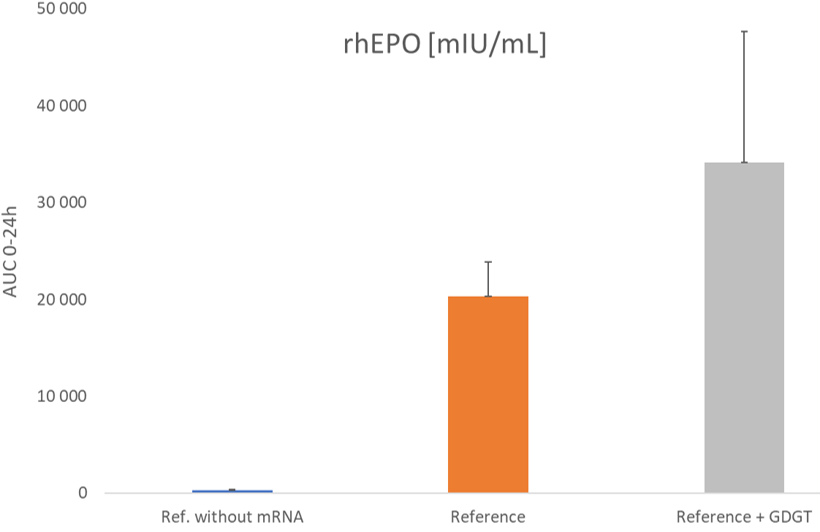
NovoArc conducted an in vivo study in rats, evaluating a commercial lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulation supplemented with its proprietary GDGT lipid. The modified formulation demonstrated a more than threefold increase in bioavailability and sustained protein expression in vivo of mRNA-encoded erythropoietin (EPO) — a clear indication of improved delivery efficiency.
The results, illustrated below, confirm the beneficial properties of tetraether-containing LNPs in both in vitro and in vivo settings, showcasing their potential as a next-generation platform for oral and systemic nucleic acid delivery.